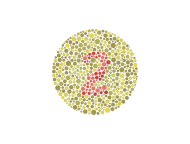Applications of This Test
The main purpose behind the making of the Munsell 100 hue test is to detect color blindness. The test records the scores and classifies them as low, average and good. The color blind score a low score of more than 100, and the people with good color visual ability have a superior score of zero.
Who Should Take This Test?
Designers and Visual Artists
The test is beneficial for artists and designers who deal with colors and their respective shades. The test helps them identify their weaknesses and helps them practice to get a good grip on the color gradation system. The Farnsworth Munsell 100 hue test helps to segregate good artists from the rest.
Color-Dependent Industries
People from the color-dependent industries, like painters, designers, makeup artists, interior designers, and decorators are in dire need of tests like the Farnsworth 100 hue test. This test helps to know the accuracy of their work and gives them a chance to work on their mistakes, if any. The test can be used as a screening test for these people to diagnose color blindness, or color deficiencies among the employees.
Personal Color Vision Assessment
The most useful function of the Munsell 100 hue test is to test personal color vision. It helps in early diagnosis of colorblindness, if one suffers from it but is unknown of the condition. Sometimes we are so overconfident that we ignore little things like calling two different shades of the color the same and fighting over it. In such conditions, this test proves to be the best test to diagnose color blindness.